Description
TCS230 8-pin SOIC surface mount package, on a single chip has 64 photodiodes. These diodes are divided into four types. 16 of the photodiode with a red filter; 16 photodiodes with a green filter; 16 photodiodes with a blue filter; the remaining 16 without any filter, may all the optical information through. The photodiode chip are staggered, it is possible that minimize non-uniformity of the incident radiation, thereby increasing the accuracy of the color recognition; on the other hand, the same color of the photodiode 16 is connected in parallel, uniformly distributed in the diode array, you can eliminate the position error color. Work by two programmable pins to dynamically select the desired filter. Typical output frequency range of the sensor from 2 Hz ~ 500 kHz, users can also select two programmable pins to 100%, 20% or 2% of the output scale factor, or power-off mode. Output scale factor so that the output of the sensor can be adapted to different measurement range and increases its ability to adapt. For example, when using a low-speed frequency counter, you can choose a small scaling value that TCS230 output frequency and counter match.
Summary:
1.imported chips TCS3200 PCB board with gold plating
2.TCS3200 is TCS230 upgrade version, the better
3.Power supply 3-5v
4.anti-light interference
5.white LED, can control the on and off.
6.can detect non-luminous object color
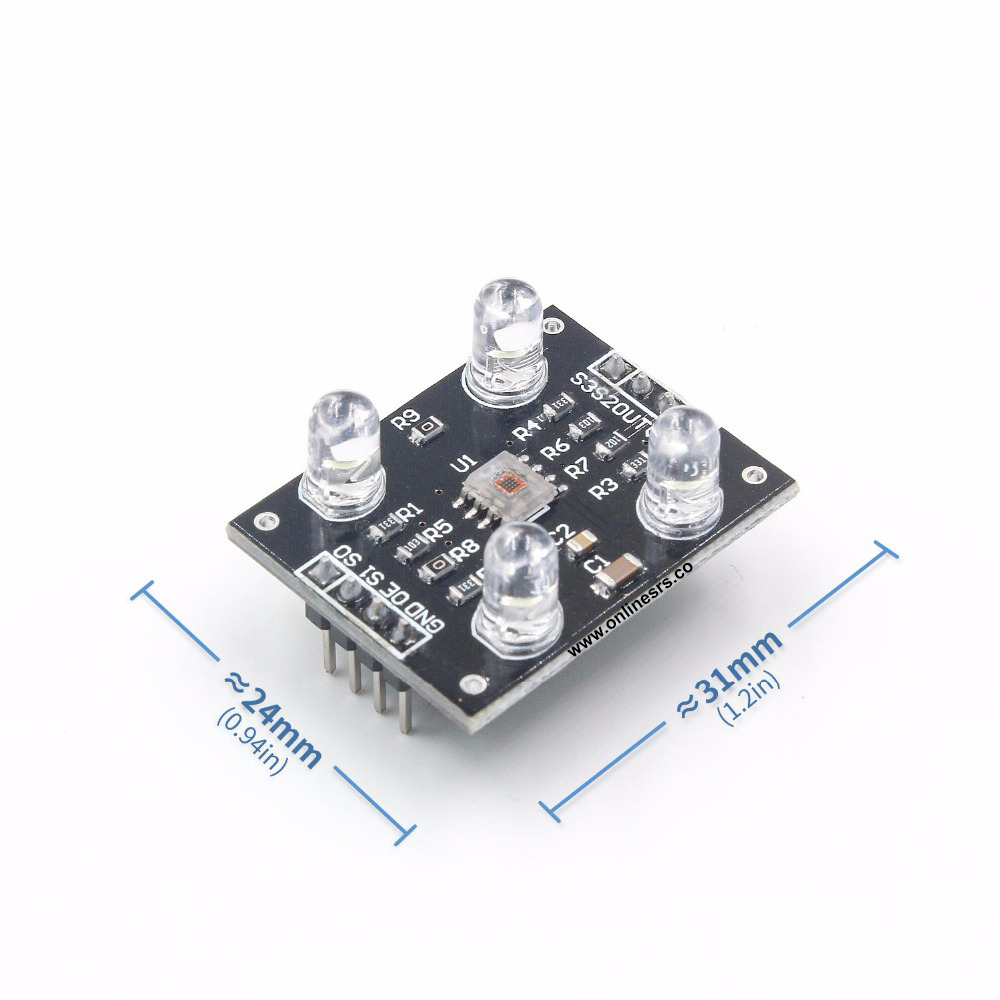
7.PCB dimensions: (L) 33mm * (W) 25mm
Simple test procedure is as follows:
#include <reg52.h>
#define uchar unsigned char
#define uint unsigned int
Duty cycle // S0, S1 to set the output; sbit S0 = P1 ^ 0
sbit S1 = P1 ^ 1;
sbit S2 = P1 ^ 3; // S2, S3 is set to consider the pattern of light
sbit S3 = P1 ^ 4;
sbit OE = P1 ^ 2; // Enable
void RS232_init ()
{
TMOD = 0X20; // Timer 1 in mode 1
SCON = 0x50;
PCON = 0X80; //
TH1 = TL1 = 0XFF; // 22.1184M crystal, the baud rate is set to 115200
TR1 = 1;
TI = 0;
RI = 0;
}
void send_char (uchar a) // send data
{
SBUF = a;
while (TI == 0);
TI = 0;
}
uchar get_char () // receiving data
{
while (RI == 0);
RI = 0;
return SBUF;
}
uint color_display (uchar m)
{
uint time, a;
a = m;
TMOD = 0x61; // counter 1, Timer 0 is operating in 16-bit mode
TH0 = TL0 = 0; // start counting from zero, the timing
TH1 = TL1 = 0;
S0 = 1;
S1 = 1;
S2 = m & 0x01;
S3 = m & 0x02;
OE = 0;
TR0 = TR1 = 1;
while (TL1 <250);
TR1 = TR0 = 0;
OE = 1;
time = TH0 * 256 + TL0;
return (time);
}
void main ()
{uint temp;
RS232_init ();
OE = 1;
while (1)
{ temp = color_display (get_char ());
RS232_init ();
send_char (temp / 1000);
send_char (temp% 1000/100);
send_char (temp% 100/10);
send_char (temp% 10);
}
}
Through the serial port to select the type of color channels, and then due to the different colors corresponding to different time (count value of the same), to determine the different colors.









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.